Applications of Graphene in Smart Textiles
Graphene, a groundbreaking material with remarkable properties such as high conductivity, flexibility, and strength, is revolutionizing the textile industry. In the realm of smart textiles, graphene is enabling the development of advanced wearable technology, temperature-regulating fabrics, and sensor-embedded clothing. These innovations have significant implications for fashion, healthcare, sports, and military applications.
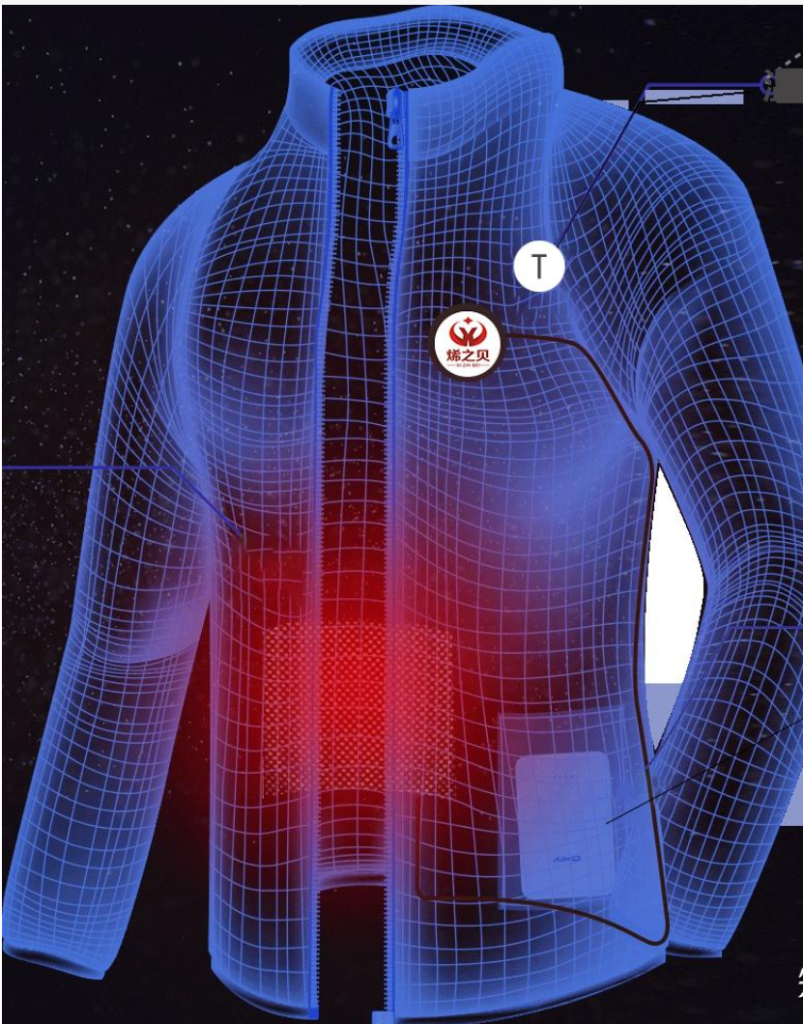
1. Graphene’s Unique Properties for Smart Textiles
Before diving into its applications, it’s important to understand the properties of graphene that make it an ideal material for smart textiles:
- High Electrical Conductivity: Perfect for integrating electronic functions into fabrics.
- Flexibility and Lightweight: Essential for wearable applications.
- Thermal Conductivity: Enables temperature regulation in garments.
- Durability: Enhances the lifespan of textiles under physical stress.
- Biocompatibility: Safe for prolonged skin contact, crucial for wearable healthcare devices.
2. Applications in Smart Textiles
2.1 Smart Clothing for Temperature Regulation
- Graphene’s Role:
- Graphene’s excellent thermal conductivity allows it to dissipate heat efficiently.
- It can be integrated into fabrics to enable temperature modulation based on the wearer’s needs or external conditions.
- Practical Uses:
- Heated Jackets: Thin graphene layers embedded in jackets can provide warmth without bulky insulation.
- Sportswear: Cooling properties for athletes during high-intensity activities.
- Seasonal Clothing: Smart fabrics that adjust warmth dynamically, making them wearable year-round.
2.2 Wearable Sensors for Health Monitoring
- Graphene-Based Sensors:
- Highly sensitive to changes in pressure, temperature, or chemical composition.
- Integrated directly into fabrics to monitor physiological parameters like heart rate, body temperature, and hydration levels.
- Applications:
- Healthcare: Continuous monitoring of vital signs for patients with chronic conditions.
- Fitness: Real-time tracking of performance metrics such as sweat composition and muscle exertion.
- Baby Care: Smart baby clothes to monitor temperature or detect illnesses early.
2.3 Energy Harvesting and Storage in Wearables
- Energy Solutions:
- Graphene’s conductivity enables textiles to function as energy harvesters, converting motion or body heat into usable electricity.
- Lightweight, flexible graphene supercapacitors can store energy generated by wearables.
- Applications:
- Self-Powered Devices: Clothing that powers LEDs, sensors, or small electronics.
- Military Gear: Self-sustaining uniforms with integrated communication devices or night-vision equipment.
2.4 Conductive Fabrics for Connectivity
- Graphene Threads and Coatings:
- Conduct electricity without compromising fabric flexibility.
- Serve as pathways for transmitting data in IoT-connected wearables.
- Applications:
- Fashion: Light-up garments or interactive designs.
- Smart Homes: Clothing that interacts with home automation systems, like turning on lights or controlling temperature.
2.5 Antimicrobial and Antistatic Properties
- Graphene’s Features:
- Natural antimicrobial properties prevent odor buildup and infections.
- Antistatic properties enhance safety and comfort, especially in industrial environments.
- Applications:
- Medical Textiles: Graphene-coated hospital gowns and bedding for infection control.
- Everyday Wear: Clothing that remains fresh longer, reducing the need for frequent washing.
3. Integration Methods
3.1 Coating and Printing Techniques
- Graphene inks can be printed directly onto fabrics to create conductive pathways.
- Spray-coating methods enable uniform application of graphene layers on textiles.
3.2 Graphene Yarns
- Spinning graphene into yarns allows it to be woven into fabrics.
- Produces durable, washable, and flexible smart textiles suitable for daily use.
3.3 Hybrid Materials
- Combining graphene with polymers enhances the mechanical and electrical properties of fabrics.
- Hybrid solutions optimize functionality without sacrificing comfort.
4. Advantages Over Traditional Materials
- Versatility: Unlike metals, graphene offers conductivity without adding bulk or weight.
- Environmental Sustainability: Graphene-based coatings are less toxic and more environmentally friendly than traditional conductive materials.
- Durability: Graphene-infused textiles are more resistant to wear and tear, making them ideal for long-term use.
5. Challenges in Adoption
5.1 Production Scalability
- Manufacturing large quantities of graphene at low cost remains a challenge.
- Innovations like roll-to-roll graphene production aim to address this issue.
5.2 Fabric Integration
- Ensuring graphene coatings remain intact after washing or prolonged use requires further research.
- Improving adhesion between graphene layers and textile fibers is critical.
5.3 Market Awareness
- Educating end-users about the benefits and care of graphene-enhanced textiles is essential for widespread adoption.
6. Future Outlook
6.1 Expansion into Consumer Markets
- As production costs decrease, graphene smart textiles will become more affordable for everyday consumers.
- Potential for integration into mainstream fashion, making wearable tech ubiquitous.
6.2 Growth in Specialized Industries
- Healthcare: Demand for health-monitoring wearables is driving graphene research in this sector.
- Defense: Military uniforms with multi-functional capabilities, including energy storage and temperature control.
- Sports: Professional athletes will benefit from graphene-enhanced performance gear.
6.3 Sustainability Focus
- Graphene textiles align with sustainability trends, as they offer long-lasting, multifunctional solutions that reduce waste.
7. Conclusion
Graphene’s integration into smart textiles is reshaping the future of wearable technology. Its unparalleled properties—conductivity, flexibility, and durability—make it a game-changer for applications in temperature regulation, health monitoring, and interactive clothing. While challenges like scalability and integration persist, ongoing advancements in graphene production and textile engineering promise a bright future. From healthcare to fashion, graphene-enabled textiles are paving the way for a smarter, more connected world.

