Carbon Nanotube Q&A Series: Educational Insights with Customer Interaction
Welcome to our “CNT Knowledge Hub”, where we answer the most frequently asked questions about carbon nanotubes in a clear, engaging, and technically sound way. Whether you’re an engineer, researcher, product developer—or simply curious—this series is designed to make CNTs more accessible and understandable to everyone.
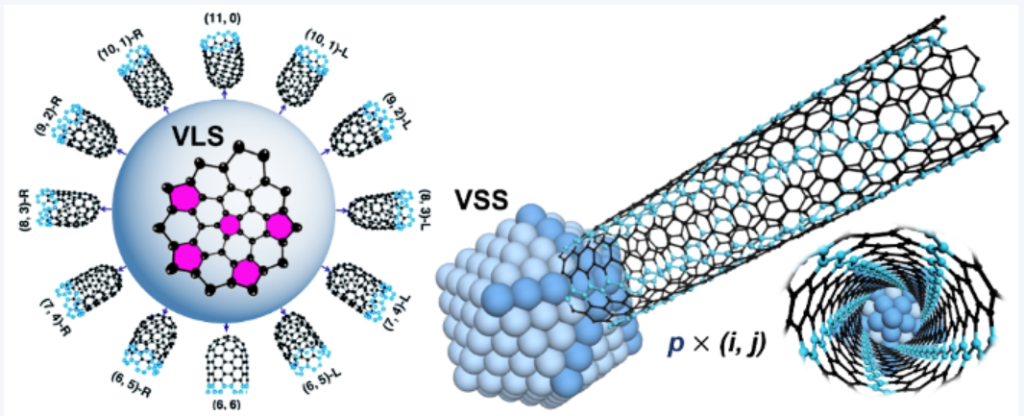
Q1: What exactly are carbon nanotubes (CNTs)?
A: Carbon nanotubes are cylindrical nanostructures made of rolled-up sheets of graphene. They can be single-walled (SWCNTs) or multi-walled (MWCNTs). CNTs are famous for their ultra-high strength, excellent electrical conductivity, and exceptional thermal stability.
🧠 Fun Fact: CNTs are over 100 times stronger than steel by weight, yet extremely lightweight.
Q2: What makes CNTs so special compared to other materials?
A:
-
Strength-to-weight ratio: Unmatched in structural materials.
-
Electrical conductivity: Ideal for batteries, electronics, and sensors.
-
Thermal conductivity: Great for heat dissipation in electronics.
-
Flexibility: Key to applications like flexible displays and wearable electronics.
🔍 Keyword Insight: “High-performance nanomaterials” and “conductive nanofillers” are hot search terms in this context.
Q3: How are CNTs used in real-world applications?
A:
-
Energy: As conductive additives in lithium-ion and solid-state batteries.
-
Aerospace: Lightweight structural composites.
-
Construction: To improve cement strength and reduce cracking.
-
Textiles: For smart fabrics and wearable electronics.
-
Healthcare: For biosensors, drug delivery, and bio-imaging.
Q4: Are CNTs safe for humans and the environment?
A: CNTs are generally safe when properly handled and embedded in matrices (like polymers or coatings). However, inhalation of dry CNT powders during manufacturing may pose respiratory risks. Proper safety protocols and protective equipment are essential.
✅ Best Practice Tip: Use sealed mixing, local ventilation, and PPE during handling.
Q5: What’s the difference between SWCNTs and MWCNTs?
| Feature | SWCNT (Single-Walled) | MWCNT (Multi-Walled) |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Single graphene cylinder | Multiple concentric cylinders |
| Conductivity | Higher | Good, but slightly lower |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Flexibility | More flexible | Stiffer |
| Use cases | Advanced electronics, biosensors | Composites, coatings, batteries |
Q6: Can CNTs replace traditional fillers like carbon black or graphene?
A: In many cases, yes. CNTs provide significantly better electrical and mechanical performance at lower loadings. For applications where space, weight, and performance are critical, CNTs are increasingly the material of choice.
📊 Example: In EV batteries, CNTs can improve energy density and reduce internal resistance more effectively than carbon black.
Q7: How do I disperse CNTs in my formulation?
A: Dispersion is one of the key challenges. Solutions include:
-
Using surfactants or dispersants (e.g., nonionic, polymeric types)
-
Ultrasonication or high-shear mixing
-
Surface-functionalized CNTs for compatibility with solvents/resins
🧪 Pro Tip: Our XFZ-series dispersants have shown excellent results in both aqueous and resin-based systems.
Q8: Where is the CNT market headed in the next 5–10 years?
A: Global demand for CNTs is projected to grow rapidly, driven by EVs, renewable energy, flexible electronics, and advanced manufacturing. Automation, cost reduction, and green production will be key to unlocking new markets.
🌍 Emerging Markets: Southeast Asia, Eastern Europe, and LATAM are rising as new hotspots.
💬 Have a Question? Ask Us!
We invite customers and readers to submit their CNT-related questions. Selected queries will be featured in future posts—along with our expert insights!
📩 Contact us at: info@graphenerich.com
Or send us a message via WhatsApp: +86 13615882924

