Graphene Current Collectors for Lithium Batteries: Boosting Performance and Efficiency
Current collectors are mediums that gather the electric current generated by the active materials in a battery, allowing for the output of a larger current. Traditional current collectors use metal materials such as copper foil and aluminum foil, but they have drawbacks like being highly reactive, prone to oxidation, and having high density—particularly copper, with a density as high as 7.9 g/cm³. Graphene macro-films, when used as current collectors, are made from graphene membranes and possess excellent properties such as high conductivity, high thermal conductivity, light weight, acid and alkali resistance, high flexibility, and fold resistance. They can replace traditional metal current collectors, improving the stability and energy density of lithium batteries.
Performance Characteristics
- High Conductivity: The conductivity of ideal graphene can reach up to 10^8 S/m.
- Lightweight: Reduces the overall device weight.
- Flexibility: The unique 2D carbon material structure gives it excellent flexibility.
- High Thermal Conductivity: Effectively dissipates heat from within the battery, ensuring high safety.
- Mechanical and Electrical Stability: High mechanical stability and consistent resistance.
- Reduced Cathode Polarization: Graphene membranes as current collectors reduce cathode polarization and slightly enhance the cycle and rate performance of the cathode.
- Improved Anode Capacity: When used as an anode current collector, the capacity increases significantly, which can markedly boost the overall energy density of the battery.
- Graphene Macro-Film vs. Copper Foil
| Characteristic | Graphene Macro-Film | Metal Copper Foil |
| Conductivity (S/m) | 1×10^0~0.12×10^7 (controllable) | 1.3×10^7 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) | 1200-5000 | 398 |
| Density (g/cm³) | 0.4-2.1 | 8.9 |
| Mechanical Stability (folding) | 100,000 times without change | 12 times, breaks |
| Chemical Stability | Stable, corrosion-resistant | Dissolves in acid, easily oxidized |
| Flexibility | Good | Poor |
Microstructure
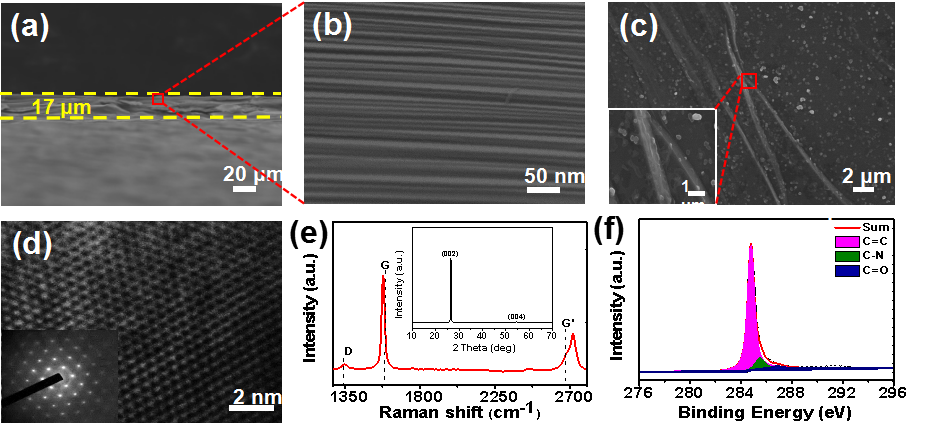
Mechanism of Action
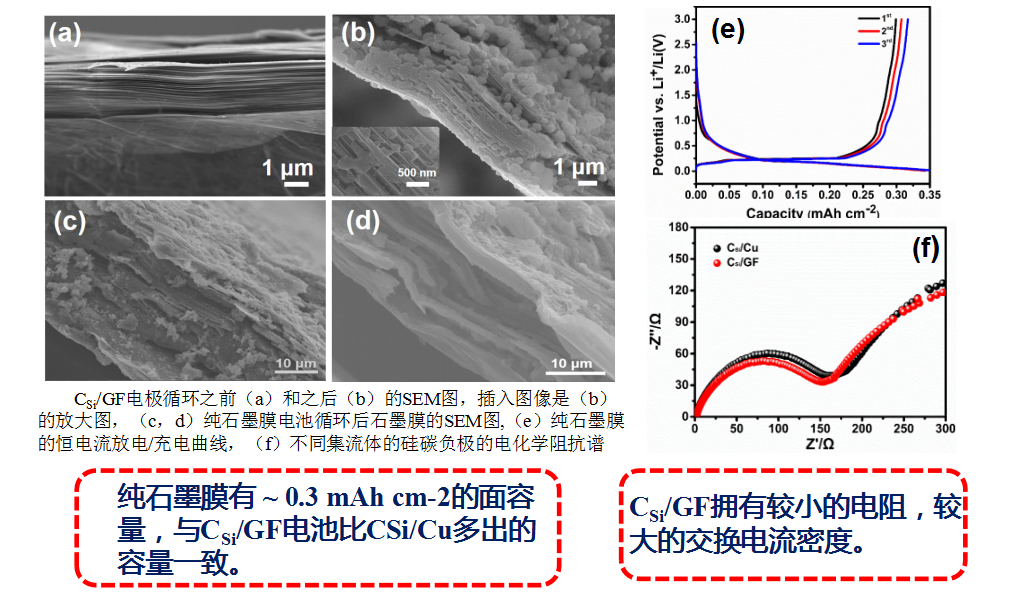
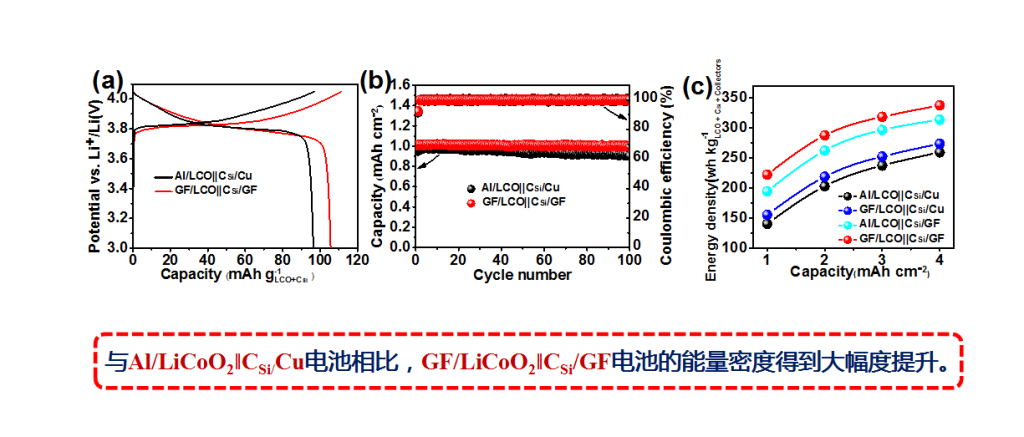
Technical Specifications
| Parameter | HXGCC-8 | HXGCC-10 | HXGCC-12 | HXGCC-15 | Test Method |
| Thickness (μm) | 8 ± 0.6 | 10 ± 0.6 | 12 ± 0.6 | 15 ± 1 | ASTM D374 |
| Conductivity (S/m) | 1.2 × 10^6 | 1.2 × 10^6 | 1.2 × 10^6 | 1.2 × 10^6 | ASTM E1269 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | ≈1220 | ≈1220 | ≈1220 | ≈1220 | ASTM E1461 |
| Density (g/cm³) | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 1.8 ± 0.1 | ASTM E1269 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 30 | 50 | 60 | 80 | GB/T 1040.3-2006 |
| Elongation (%) | ≥2.5% | ≥2.5% | ≥2.5% | ≥2.5% | GB/T 1040.3-2006 |
| Pinhole Count (per m²) | ≤20 holes/m²; diameter ≤0.3mm | ≤20 holes/m²; diameter ≤0.3mm | ≤20 holes/m²; diameter ≤0.3mm | ≤15 holes/m²; diameter ≤0.3mm | Image analyzer |
| Bending Cycles (R1/180˚) | > 100,000 | > 100,000 | > 100,000 | > 100,000 | GB/T 2792-2014 |

