Water Quality Monitoring: The Application of Graphene Sensors in Detecting Heavy Metal Ions, Microorganisms, and Chemical Pollutants
Clean water is essential for human health, agriculture, and ecosystems. However, water contamination remains a significant global challenge, caused by industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and inadequate wastewater management. Traditional water monitoring techniques, while effective, often involve time-consuming and costly processes requiring laboratory analysis. This is where graphene-based sensors step in, providing a revolutionary, cost-effective, and highly sensitive approach to real-time water quality monitoring.
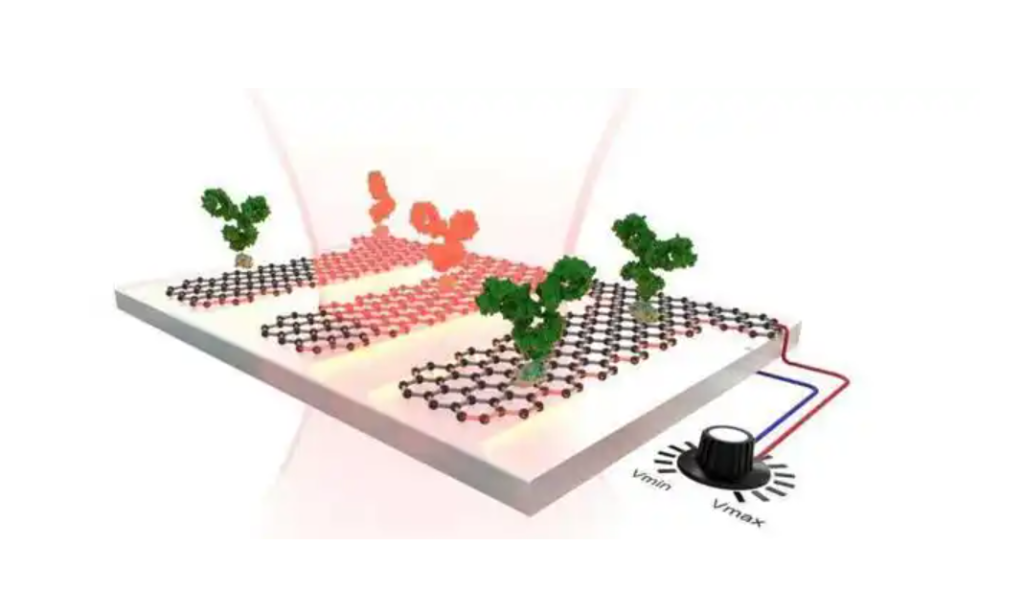
Why Graphene is Ideal for Water Quality Monitoring
Graphene, a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, boasts exceptional physical and chemical properties that make it highly effective for detecting contaminants in water:
- High Sensitivity: Graphene’s large surface area and excellent conductivity enable it to detect even trace amounts of pollutants.
- Chemical Versatility: It can be functionalized with various molecules to target specific contaminants, including heavy metals and microorganisms.
- Durability: Graphene’s robust structure ensures it remains effective under harsh environmental conditions.
- Rapid Response Time: Graphene sensors provide instant results, making them ideal for real-time monitoring.
Applications of Graphene Sensors in Water Quality Monitoring
Graphene-based sensors are highly versatile and can detect a wide range of water contaminants:
1. Heavy Metal Ions
Heavy metals such as lead (Pb²⁺), mercury (Hg²⁺), cadmium (Cd²⁺), and arsenic (As³⁺) are toxic even at low concentrations. Graphene sensors functionalized with specific chemical groups or nanoparticles can bind to these ions, allowing precise detection.
- Example: A graphene oxide (GO) sensor modified with thiol groups can effectively detect mercury ions at sub-nanomolar levels.
2. Microorganisms
Contamination from pathogens like E. coli, Salmonella, and viruses poses serious health risks. Graphene sensors can be functionalized with antibodies, DNA, or peptides to specifically bind to microbial cells, providing a rapid and accurate detection mechanism.
- Example: Graphene field-effect transistors (GFETs) have been used to detect E. coli in water within minutes, offering faster results compared to traditional culture-based methods.
3. Chemical Pollutants
Graphene sensors can identify organic pollutants like pesticides, herbicides, and pharmaceuticals. Their high sensitivity ensures that even trace amounts are detected, which is critical for ensuring water safety.
- Example: Reduced graphene oxide (rGO) sensors are capable of detecting atrazine, a common herbicide, at parts-per-trillion (ppt) levels.
Advantages of Graphene Sensors for Water Quality Monitoring
- Real-Time Monitoring: Graphene sensors provide instant feedback, enabling proactive measures to address contamination.
- High Precision: They offer excellent accuracy, even for detecting multiple contaminants simultaneously.
- Portability: Compact designs make these sensors suitable for on-site testing in remote areas.
- Cost Efficiency: Compared to traditional methods, graphene sensors reduce the need for expensive laboratory equipment and time-intensive procedures.
- Energy Efficiency: Their low power requirements make them ideal for deployment in battery-powered or solar-powered devices.
Current Products and Technologies in Development
Several companies and research institutions are actively developing graphene-based water monitoring solutions:
1. Handheld Water Quality Testers
Portable graphene sensors are being integrated into handheld devices that can test for multiple contaminants simultaneously. These devices are useful for households, industrial plants, and environmental agencies.
2. Smart Monitoring Systems
Graphene sensors embedded in IoT-enabled systems provide continuous water quality data, which can be accessed remotely via mobile apps or cloud platforms.
3. Wearable Water Sensors
Wearable devices equipped with graphene sensors are being explored for real-time monitoring of personal hydration and exposure to contaminants.
4. Environmental Monitoring Stations
Graphene sensors are being deployed in fixed monitoring stations near rivers, lakes, and industrial discharge points to track long-term water quality trends.
Real-World Performance and Case Studies
1. Heavy Metal Detection in Rivers
A graphene-based sensor deployed in a polluted river in China successfully detected trace amounts of lead and cadmium, alerting authorities to take immediate action.
2. Pathogen Monitoring in Drinking Water
In India, researchers used graphene sensors to detect E. coli in municipal water supplies. The results demonstrated faster and more accurate detection compared to traditional microbiological tests.
3. Pesticide Detection in Agricultural Runoff
Graphene sensors integrated into an IoT system monitored pesticide levels in runoff water from farmlands in the US Midwest. The system provided real-time alerts, helping farmers implement corrective measures.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite their immense potential, graphene sensors face some challenges:
- Scalability: Mass production of high-quality graphene sensors remains a bottleneck. Advances in manufacturing technologies, such as chemical vapor deposition (CVD), are addressing this issue.
- Interference from Complex Matrices: Water samples often contain diverse substances that can interfere with sensor readings. Efforts to improve selectivity are ongoing.
- Integration with Existing Infrastructure: Retrofitting graphene sensors into current water monitoring systems can be complex and costly.
Future Prospects
- Advanced Functionalization: Developing more specific chemical groups for targeting a broader range of contaminants.
- Miniaturization: Creating ultra-compact sensors for integration into wearables and portable devices.
- Global Implementation: Increasing adoption of graphene sensors in developing countries for affordable and effective water quality monitoring.
Conclusion
Graphene sensors are poised to transform water quality monitoring by offering a fast, accurate, and cost-effective alternative to traditional methods. Their ability to detect heavy metals, pathogens, and chemical pollutants with high sensitivity makes them invaluable for ensuring safe drinking water, protecting ecosystems, and addressing industrial pollution.
As research and development continue, graphene-based water sensors will become an essential tool in the global effort to monitor and maintain water quality. By harnessing the unique properties of graphene, we can achieve a cleaner, healthier, and more sustainable future.

