Graphene in Water Desalination: Revolutionizing Membrane Technology for a Thirsty Planet
Introduction
With increasing global water scarcity, the need for efficient, scalable desalination technologies has become urgent. Traditional membranes used in reverse osmosis (RO) face limitations in throughput, fouling, and energy consumption. Enter graphene and graphene oxide (GO) membranes, which offer unprecedented water flux, selectivity, and durability thanks to their nanoscale tunability and hydrophilic surfaces.
1. How Graphene Works in Water Filtration
-
Ultra-thin Layer: Graphene’s atomically thin structure allows fast water transport
-
Nanochannels: GO sheets create precisely spaced nanochannels for selective filtration
-
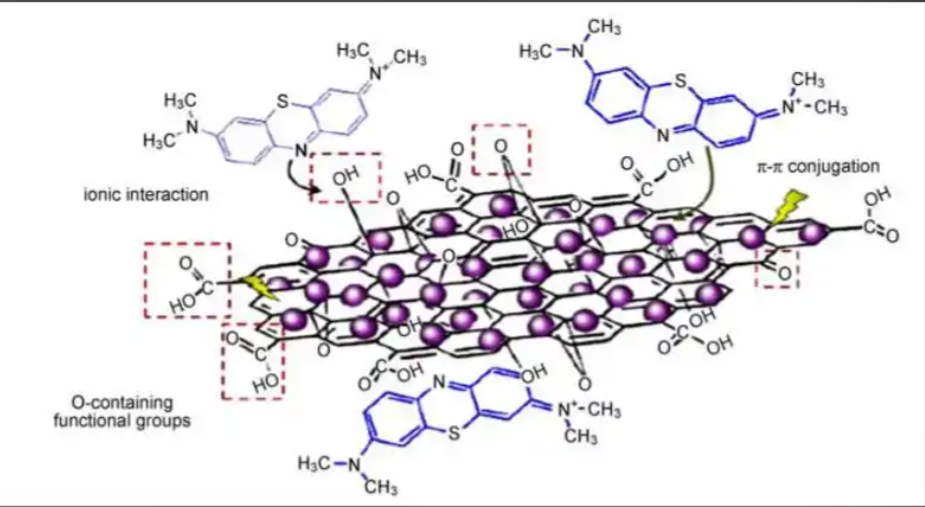
Hydrophilicity: GO’s oxygen-containing groups attract water molecules
-
Anti-fouling Properties: Smooth graphene surface resists biofilm formation
2. Graphene-Based Membrane Types
a. Graphene Oxide (GO) Membranes
-
Most studied for water treatment
-
Layer-by-layer assembled for size-selective filtration
-
Removes salts, heavy metals, and organic pollutants
b. Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO)
-
Enhanced strength and chemical resistance
-
Suitable for long-term high-pressure applications
c. Nanocomposite Membranes
-
Graphene blended with polymers (e.g., PVDF, polysulfone)
-
Improves mechanical and thermal performance
3. Advantages over Conventional RO Membranes
-
Higher Flux: Up to 50–100x water throughput at same pressure
-
Lower Energy Use: Less hydraulic resistance in graphene nanochannels
-
Greater Salt Rejection: High NaCl and divalent ion rejection efficiency
-
Longer Lifespan: Better mechanical and chemical resistance
-
Scalability: Compatible with existing membrane module formats
4. Applications and Deployment
-
Seawater Desalination: Large-scale RO plants
-
Brackish Water Treatment: Rural and inland freshwater sourcing
-
Industrial Wastewater Reuse: Electronics, textile, mining sectors
-
Point-of-Use Filters: Home or emergency water purifiers
5. Research and Commercialization
-
Lockheed Martin: Patented Perforene™ graphene membrane for RO
-
NANO SUN (Singapore): Commercial graphene ceramic filters
-
University of Manchester: Lab-scale graphene sieves for salt rejection
6. Technical and Regulatory Challenges
-
Stability Under Real-World Conditions
-
Membrane Fabrication at Scale
-
Consistency in Pore Size and Distribution
-
Cost vs Performance: Balancing graphene quality and production volume
-
Regulatory Standards: Still evolving for new membrane materials
Conclusion
Graphene-based membranes represent the next frontier in desalination and water purification, offering game-changing performance in terms of speed, efficiency, and durability. As production techniques mature and regulatory standards evolve, graphene will play a vital role in securing clean water for future generations.

